Linear Design |
Historically design has used what is referred to as a Linear approach. This is best summed up by looking at the image below: |
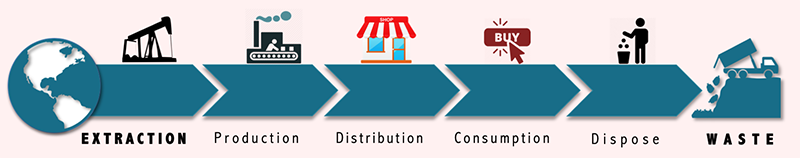 |
The obvious problem is that when a product comes to end of life it usually ends up in a Land Fill. This obviously has a negative impact upon the environment.
This Take, Make and Dispose model can also be thought of as Unsustainable Design. |
Circular Design
The aim of Circular design is to take a step back from the initial problem, take a bigger (or Zoomed out) look at the situation and try to rethink what happens to products when they are no longer needed.
As you can see from the image below, when we get to the end of the consumption stage (when a product is no longer being used), we are exploring other possibilities including reusing it (for other uses) and repairing (rather than throwing away) if the product is damaged.
It is often said that we are living in a throwaway culture because when a product no longer works, is no longer useful or appears to be out of fashion, then we simply throw it away and buy a newer one. During and after World War 2 there was a big push to reuse and repair items because there was a shortage of materials and once again governments around the world are encouraging this approach through campaigns, legislature and through education.
By replacing the disposal stage with repair, reuse, collection, recycling and recovery we are now offered the opportunity to approach designing in a different way.
The aim of Circular Design is to minimise waste and avoid duplication. This can be accomplished in a number of ways including:

|
By enabling a design to have multiple uses (therefore making it more useful and desirable) |

|
Focusing on increasing positive benefits rather than reducing negative impacts. |

|
Creating something that adds value to the ecosystem e.g. biodegradable products that break down like natural things do. |

|
Using services to replace products e.g. getting people to use a transport system instead of buying cars. |
In the simplified model below Create could mean a product being repaired, recycled, re-manufactured, reused or re-purposed (used to serve a different purpose). This model is sometimes referred to as Closed Loop because the product is continuously being re-purposed. |
